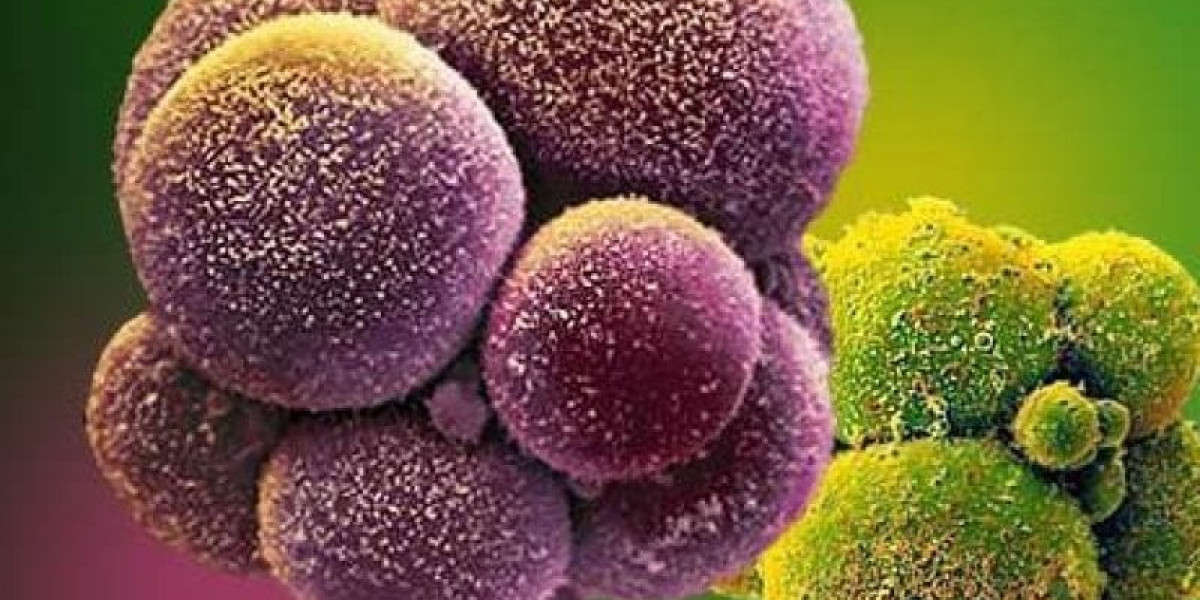
Autologous cell therapy is a promising field within regenerative medicine, involving the use of a patient's own cells for therapeutic purposes. This market has witnessed significant growth over the past decade, driven by the increasing demand for personalized and effective treatments for various diseases and conditions. The concept of autologous cell therapy is grounded in the idea that using a patient's own cells can reduce the risk of immune rejection, improve therapeutic outcomes, and enhance the overall safety profile of treatments.
Factors Driving the Growth of the Autologous Cell Therapy Market
Several key factors contribute to the rapid growth of the autologous cell therapy market. One of the primary drivers is the growing prevalence of chronic diseases and conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders. These diseases often do not have a definitive cure, making them ideal candidates for personalized therapies, which is where autologous cell therapy comes into play.
Autologous cell therapies are being used in the treatment of a variety of conditions, including hematological malignancies (like leukemia), certain types of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, and autoimmune diseases. The ability to regenerate damaged tissue and replace malfunctioning cells with healthy ones offers hope to patients suffering from conditions that traditional treatments may not address effectively.
Another important factor driving the market's growth is the growing investment in research and development (R&D) in cell-based therapies. Pharmaceutical companies, biotech firms, and research institutions are dedicating substantial resources to the development of new and advanced therapies using autologous cells. This has led to a rapid increase in the number of clinical trials involving autologous cell therapies, as well as breakthroughs in stem cell research, gene editing, and tissue engineering.
Furthermore, regulatory support and favorable government policies are also contributing to the expansion of this market. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have begun to create more structured frameworks for the approval of autologous cell therapies. These regulatory efforts have made it easier for companies to bring their innovations to market, ultimately benefiting patients in need of cutting-edge treatments.
Key Applications of Autologous Cell Therapy
The autologous cell therapy market spans a wide range of applications, with several prominent therapeutic areas gaining attention. One of the most notable applications is in oncology. Autologous cell therapies are used in cancer treatments, particularly in immune cell therapies such as CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell) therapy. This therapy involves modifying a patient's own T-cells to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. CAR-T therapy has demonstrated remarkable success in treating certain types of leukemia and lymphoma, and research is ongoing to explore its use in other cancers.
In addition to cancer, autologous cell therapy has found significant applications in the field of regenerative medicine. Conditions like osteoarthritis, cartilage defects, and other musculoskeletal disorders have been treated using autologous stem cell therapy, where a patient's own stem cells are harvested, processed, and then injected back into the affected area to promote tissue regeneration and repair. This approach helps reduce inflammation, stimulate healing, and restore damaged tissues.
Moreover, autologous cell therapy is also making strides in treating cardiovascular diseases, where it is used to regenerate damaged heart tissue following a heart attack. By using the patient’s own cells to promote tissue repair, autologous therapy reduces the chances of rejection and enhances the overall efficacy of treatment. Additionally, this therapy is being researched for its potential to treat neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and spinal cord injuries, where it aims to replace lost neurons and restore normal function.
Challenges and Barriers to Growth
While the autologous cell therapy market shows significant potential, there are several challenges that need to be addressed for sustained growth. One of the primary barriers is the complexity and cost of production. Autologous cell therapies often require highly specialized facilities and processes for cell collection, processing, and reinjection, making them expensive to produce. The high cost of these therapies can limit their accessibility to a broader patient population, which can slow market adoption.
Another challenge is the regulatory hurdles involved in bringing autologous therapies to market. Despite regulatory advancements, the approval process for cell-based therapies can still be lengthy and complex, requiring extensive clinical data to demonstrate safety and efficacy. This regulatory landscape can delay the introduction of new therapies and increase costs for companies involved in the development of autologous cell treatments.
Moreover, there are logistical challenges related to the transportation and storage of autologous cells. Since these therapies require the use of a patient’s own cells, there is a need for careful handling and timely processing. This can make it difficult to scale production and ensure the widespread availability of these therapies.
Market Outlook
Despite these challenges, the outlook for the autologous cell therapy market remains positive. The continued advancements in stem cell research, gene editing technologies, and tissue engineering are expected to open up new avenues for the use of autologous cell therapies. Additionally, the increasing demand for personalized medicine and the growing number of patients with chronic conditions will continue to fuel market growth.
As technology advances and production techniques become more efficient, the cost of autologous cell therapies may decrease, making them more accessible to a broader patient population. With ongoing research, regulatory support, and increased funding, the autologous cell therapy market is poised for continued expansion in the coming years, potentially transforming the landscape of modern medicine and offering new hope to patients worldwide.
read more:
| https://www.pristinemarketinsights.com/autologous-cell-therapy-market-report |