views
How Zero Discharge Systems Work: A Step-by-Step Explanation
What Are Zero Discharge Systems?
Zero Discharge Systems (ZDS) are innovative wastewater treatment systems designed to ensure that no liquid waste leaves an industrial facility. Every drop of water used in the process is either treated and reused or transformed into a solid waste that can be safely managed. As industries worldwide face increasing pressure to meet environmental standards, ZDS offers a sustainable solution to water pollution and resource depletion.
Understanding the Basics of Zero Discharge Systems
Unlike conventional wastewater treatment, which may release treated water into the environment, Zero Discharge Systems aim to achieve a closed-loop process. In this system, all water is recovered, and any impurities or contaminants are separated as solids. This approach ensures minimal environmental impact and promotes efficient resource utilization.
Definition and Key Features of ZDS
A Zero Discharge System refers to a setup where no industrial effluent is discharged into the environment. Instead, treated water is recycled internally, and the remaining waste is managed in solid form. Key features include:
-
High water recovery rate (often above 95%)
-
Efficient separation of solids and salts
-
Advanced multi-stage treatment processes
-
Compliance with stringent discharge regulations
Importance of Zero Discharge in Modern Industries
Today, industries must balance production efficiency with environmental responsibility. Governments are enforcing stricter wastewater discharge norms, and communities are more aware of ecological risks. Importance of Zero Discharge in Modern Industries :
-
Avoid penalties and shutdowns
-
Reduce their water footprint
-
Improve corporate sustainability
-
Maintain good relations with local communities
In many water-stressed regions, zero discharge is not just a best practice—it’s a necessity.
Common Applications of ZDS
Zero Discharge Systems are increasingly used in sectors where water contamination is high and regulatory pressure is strict. Common industries include:
-
Textile and dyeing units
-
Pharmaceuticals and chemical plants
-
Oil refineries
-
Power generation stations
-
Food and beverage processing units
-
Electronics and semiconductor manufacturing
These industries deal with complex wastewater streams that require advanced treatment to meet ZLD (Zero Liquid Discharge) standards.
Step-by-Step Guide to Zero Discharge Systems
The Zero Discharge Process Explained
Here’s how a typical Zero Discharge System functions:
-
Wastewater Collection and Testing: All industrial wastewater is collected and tested to determine the levels of contaminants, pH, and chemical composition.
-
Primary Filtration and Screening: Large particles and suspended solids are removed through mechanical filters and screens.
-
Chemical Treatment: Coagulants and flocculants are added to separate dissolved impurities and form sludge.
-
Biological Treatment (if applicable): Organic materials are broken down by bacteria in aeration tanks to reduce biochemical oxygen demand (BOD).
-
Membrane-Based Separation: Technologies like Ultrafiltration (UF) and Reverse Osmosis (RO) remove dissolved salts and micro-contaminants.
-
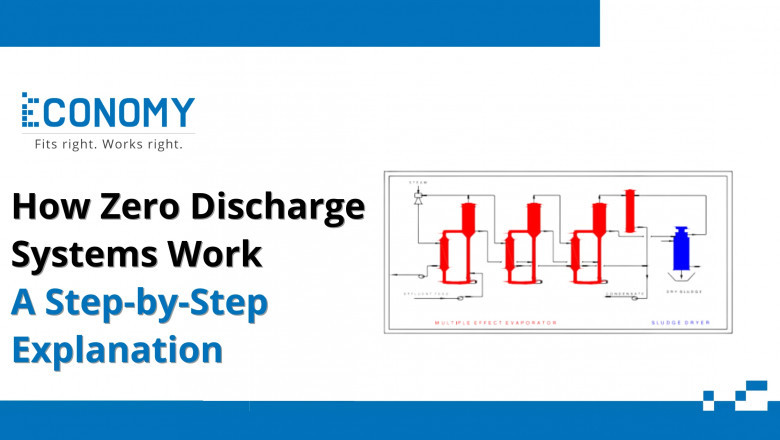
Evaporation and Crystallization: Concentrated brine from RO is sent to evaporators or crystallizers to recover water and extract salts as solid waste.
-
Water Reuse: The recovered clean water is reused in industrial processes such as cooling, washing, or as boiler feed.
Technologies Behind Zero Discharge Systems
ZDS systems use a combination of mechanical, chemical, and thermal technologies to achieve maximum efficiency:
-
UF and RO membranes for removing fine particles and salts
-
Multi-effect Evaporators (MEE) for water recovery from brine
-
Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) for energy-efficient evaporation
-
Sludge dryers and centrifuges for drying and solidifying waste
-
Automation and sensors for real-time system monitoring
The integration of these technologies varies based on the industry, wastewater type, and desired recovery rate.
Key Equipment and Processes in ZDS
Essential equipment includes:
-
Equalization tanks for flow regulation
-
Dosing units for chemical treatment
-
Membrane filtration units
-
Thermal evaporators and crystallizers
-
Sludge handling systems
-
Water recycling pipelines
The layout is often modular, allowing customization and scalability depending on the facility’s size and needs.
Benefits of Adopting Zero Discharge Systems
Implementing ZDS brings multiple long-term benefits:
-
Environmental protection by eliminating liquid discharge
-
Water savings through internal recycling and reuse
-
Operational stability by minimizing water-related disruptions
-
Regulatory compliance with current and future discharge laws
-
Corporate reputation as a sustainable and eco-friendly business
Though initial investment is higher, ZDS often results in operational cost savings over time.
Why Zero Discharge Systems Are Essential
In an age where water scarcity, pollution, and climate concerns are rising, ZDS is no longer an optional upgrade—it’s a strategic necessity. For industries with high water usage and pollutant output, adopting zero discharge systems is a proactive step toward resilience and long-term sustainability.
Case Studies: Industries Successfully Using ZDS
-
India’s textile sector, especially in Tirupur, has adopted ZDS on a large scale to restore groundwater quality and meet court-mandated regulations.
-
Middle Eastern oil refineries use ZDS to recycle process water in arid environments, reducing dependence on external water sources.
-
Global electronics manufacturers have integrated ZDS into chip fabrication units to manage high-purity water requirements and prevent discharge.
Real-World Examples of Zero Discharge Systems
-
A pharmaceutical plant in Hyderabad reduced its freshwater consumption by over 85% after implementing a membrane-evaporator-crystallizer ZDS loop.
-
A food processing plant in Europe installed ZDS to treat nutrient-rich wastewater, recover clean water, and reuse organic solids as bio-compost.
Conclusion
Zero Discharge Systems offer a forward-thinking solution for industries committed to sustainability, water conservation, and regulatory compliance. By treating and reusing every drop of water, these systems help reduce waste, save costs, and protect the environment. As industries evolve to meet the demands of the future, ZDS will remain a cornerstone of responsible and efficient industrial water management.












Comments
0 comment