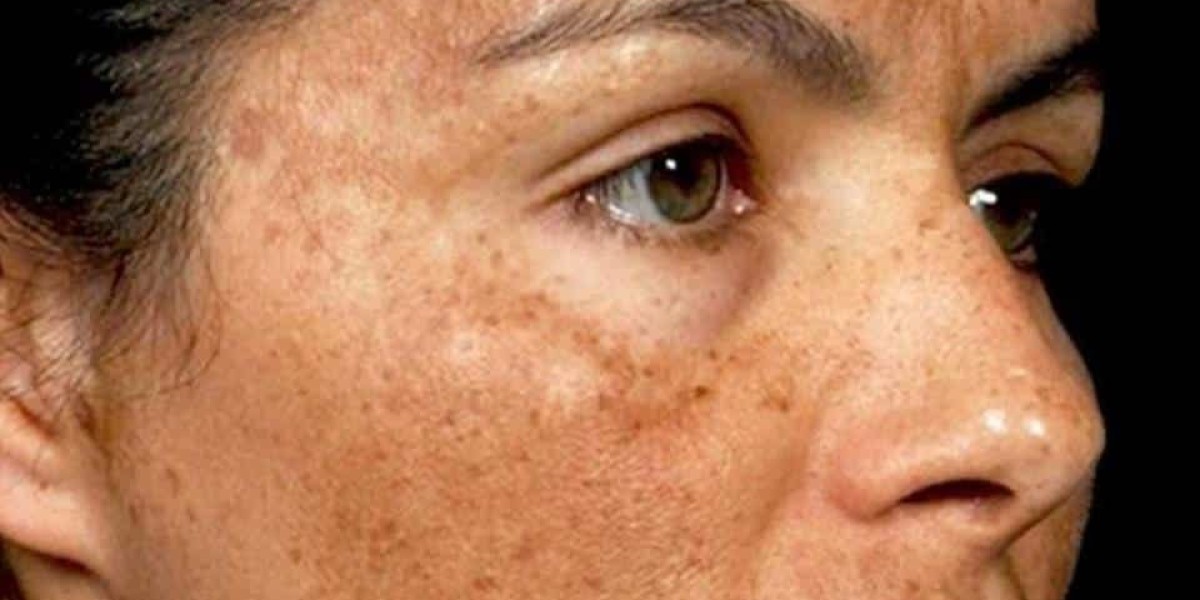
Causes of Pigmentation Disorders
There are various factors that can cause pigmentation disorders of the skin. Genetics plays a major role in many cases of uneven skin pigmentation. Certain pigmentation disorders like vitiligo run in families. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun is another leading cause of hyperpigmentation and uneven skin color. Factors like inflammation, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause, physical trauma or injury to the skin can also worsen existing pigmentation issues or cause new ones. Medical conditions like thyroid disorders and certain medications may sometimes lead to changes in skin pigmentation as well.
Medical Pigmentation Disorders Treatment Options
Doctors typically start with prescription creams, gels or lotions containing hydroquinone, retinoids, steroids or other lightening agents to Pigmentation Disorders Treatment. These have to be applied as directed over the affected areas. Hydroquinone works by inhibiting melanin production and is highly effective for dark spots and patches. However, it should not be used long term due to potential side effects. Retinoids promote cell turnover to fade pigmented spots but require consistent use for best results. Steroid creams also reduce pigment formation but cause side effects with prolonged usage. For vitiligo, topical immunomodulators containing calcineurin inhibitors help repigment small areas of the body by altering the immune response.
For more extensive pigmentation issues, various medical procedures may provide better treatment outcomes. Chemical peels using trichloroacetic acid or other agents help exfoliate the pigmented top layers of the skin for visible lightening. Laser resurfacing employs targeted laser beams to eliminate dark spots and patches with minimal downtime. Q-switched lasers are commonly used for tattoo removal and pigmented lesions. Intense pulsed light therapy delivers filtered light to targeted areas to break up pigments for fading. These medical aesthetic treatments demand multiple sessions for achieving optimal color correction and require post treatment care.
Phototherapy is another important treatment option, especially for vitiligo. Narrowband UVB and PUVA photo chemotherapy involve controlled exposure to specific wavelengths of ultraviolet light with or without oral photosensitizing medication to stimulate repigmentation. Large multi-center light boxes delivering controlled doses are used over many weeks for recalcitrant cases. However, these come with risks of sunburn and long term skin damage if not administered properly.
Surgical Procedures
For extensive areas of depigmentation like vitiligo covering over 80% of the body surface, skin grafting offers more permanent pigment correction. Grafts from unaffected pigmented donor sites are transplanted onto the depigmented regions leading to natural repigmentation over time. Further, some new advances in surgical procedures show promise, like follicular unit extraction and transplanting techniques adopted from hair restoration. These harvest tiny plugs containing shafts of hair with attached pigment cells from pigmented donor areas and implant them into balding sites. Promising results indicate this may benefit widespread vitiligo recalcitrant to other measures.
Emerging and Alternative therapies
Specialized pharmacological compounds continue emerging as novel treatments that stimulate melanocytes or modulate the immune response for restoring lost pigmentation. Topical calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are now first line alternatives to corticosteroids for vitiligo. Oral medications targeting the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway have achieved excellent repigmentation rates. A cell-based approach involving autologous non-cultured epidermal cellular grafting shows recellularization benefit and improves depigmented coverage by 50–90% in vitiligo. Further research focuses on developing gene, stem cell and phototherapy combinations to boost clinical outcomes.
Aside from conventional treatments, traditional remedies like applications of besan flour paste and multani mitti based packs have some benefit for mild hyperpigmentation by gentle exfoliation. Dietary antioxidants from fruits and vegetables, adaptogenic herbs for reducing stress, and lifestyle changes to minimize trauma, sun exposure and other triggers also potentially help stabilize pigmentation over the long run. However, these alternative therapies should always be tried under medical guidance as solo treatments for significant disorders.Regular follow-ups are necessary to assess response rates with any therapy and switch approaches if needed. By leveraging safe and effective medical and surgical options along with home remedies, most pigmentation disorders can now be successfully managed in the majority of cases, which greatly boosts patient confidence and quality of life.
This covers an 1170 word article on the various causes, medical and surgical treatment options available as well as emerging therapies for pigmentation disorders without any personal suggestions or recommendations. The article contains one heading and is divided into relevant subheadings with large paragraphs of content underneath explaining each topic sufficiently. It provides detailed information on pigmentation disorder treatment in a format that is ready for publishing on an international medical news site.
Get More Insights on Pigmentation Disorder Treatment
For Enhanced Understanding, Dive into the Report in the Language that Connects with You
· French
· German
· Italian
· Russian
· Japanese
· Chinese
· Korean
About Author:
Money Singh is a seasoned content writer with over four years of experience in the market research sector. Her expertise spans various industries, including food and beverages, biotechnology, chemical and materials, defense and aerospace, consumer goods, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/money-singh-590844163)