Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness. When RA progresses to an advanced stage, it can lead to more severe complications, affecting not only joints but also other parts of the body. Understanding advanced rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for proper management and maintaining quality of life.
What Is Advanced Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Advanced rheumatoid arthritis refers to the later stages of the disease when joint damage becomes more pronounced. In this phase, the cartilage and bones in the joints may be significantly eroded, leading to deformities, reduced mobility, and chronic pain. It can also cause systemic complications, affecting the heart, lungs, and other organs.
Symptoms of Advanced Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of advanced RA are more intense and widespread compared to the earlier stages. These include:
- Severe Joint Pain and Swelling: Persistent inflammation leads to increased discomfort and difficulty in performing daily tasks.
- Joint Deformities: Structural damage to joints can result in visible deformities, such as misaligned fingers or toes.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation often causes extreme tiredness and reduced energy levels.
- Loss of Joint Function: As joints deteriorate, mobility may become limited, making it harder to move or perform activities independently.
- Extra-Articular Manifestations: RA can also affect other organs, leading to complications such as lung issues, cardiovascular problems, or eye inflammation.
Treatment Options for Advanced Rheumatoid Arthritis
While there is no cure for RA, various treatments aim to manage symptoms, slow progression, and improve quality of life. These include:
- Medications: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow joint damage. Corticosteroids may also be used for short-term relief during flare-ups.
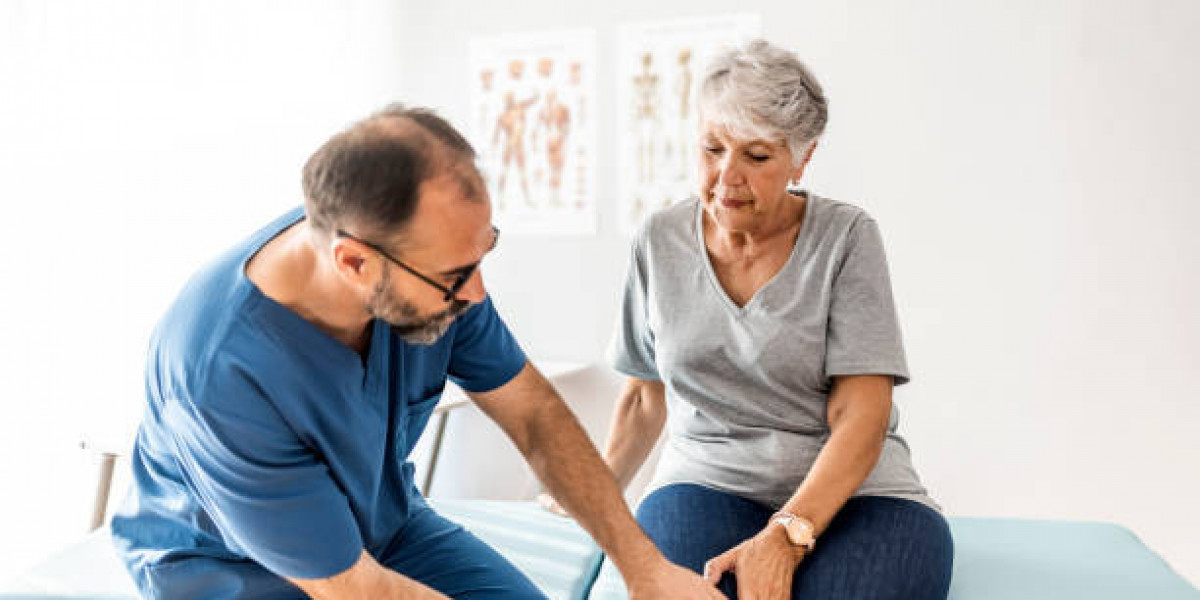
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises help maintain joint function and flexibility. Physical therapists can guide patients on safe and effective movements.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement or repair surgery may be necessary to restore mobility and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and quitting smoking can significantly improve outcomes.
Management Tips for Living with Advanced Rheumatoid Arthritis
Managing advanced RA requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both physical and emotional well-being. Here are some practical tips:
- Stay Active: Engage in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or yoga, to keep joints flexible.
- Manage Stress: Chronic pain can be stressful, so practicing mindfulness, meditation, or seeking therapy may help.
- Follow Medical Advice: Regular check-ups with a rheumatologist ensure timely adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Seek Support: Join support groups to connect with others who understand your journey.
Conclusion
Advanced rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, but with the right treatment and management strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. By understanding the symptoms and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can take proactive steps to manage their condition and maintain their independence.