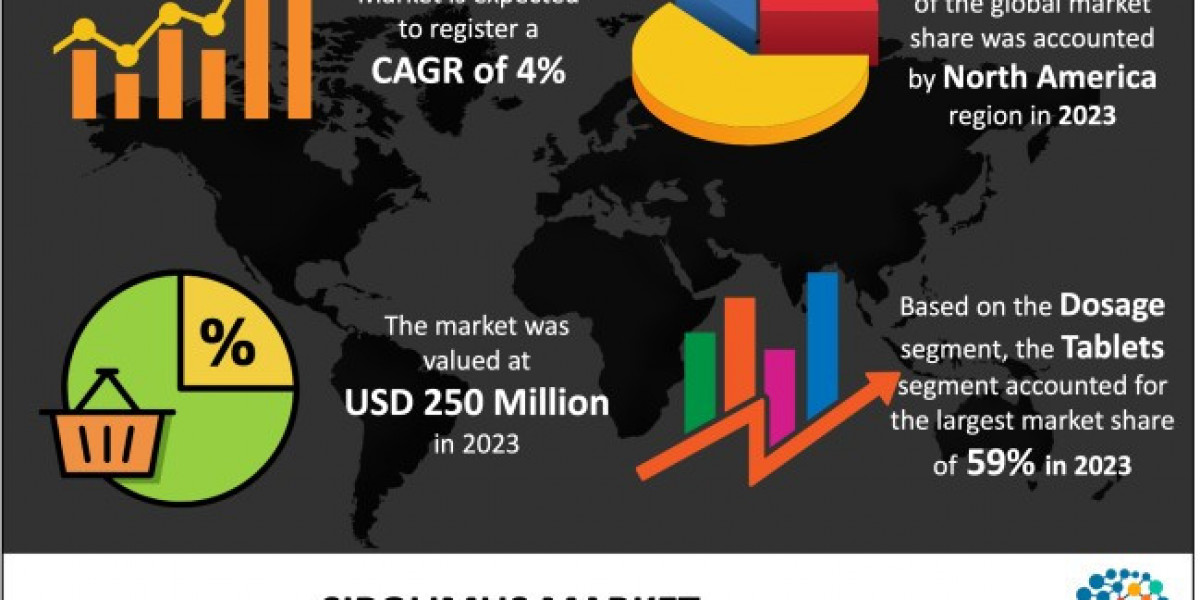
The heat-reflecting paints market has witnessed considerable growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions in construction and urban planning. These paints are designed to reflect sunlight, reduce heat absorption, and improve the energy efficiency of buildings. However, like any emerging market, the heat-reflecting paints sector faces several threats that could impede its growth and profitability. These challenges are primarily related to competition, cost concerns, regulatory issues, and market awareness. In this article, we explore the key threats affecting the heat-reflecting paints market and the strategies companies can adopt to mitigate them.
1. Competition from Alternative Cooling Technologies
One of the primary threats to the heat-reflecting paints market comes from alternative cooling technologies and materials. As the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable solutions rises, consumers and businesses are increasingly turning to other methods to reduce heat absorption and lower cooling costs. These alternatives include reflective roof membranes, cool roofs, solar reflective films, and high-performance insulation materials.
While heat-reflecting paints are a proven solution, these alternative technologies may provide superior performance in certain environments or offer a broader range of benefits. For example, cool roofs can provide not only heat reflection but also enhanced durability and protection against weathering. This growing competition from alternative cooling products may limit the market share of heat-reflecting paints, particularly in regions where other solutions are more effective or widely accepted.
2. High Initial Cost and Consumer Reluctance
Heat-reflecting paints can be significantly more expensive than conventional paints, especially in terms of materials and application. This price difference can be a significant barrier for many consumers, particularly in price-sensitive markets. While heat-reflecting paints offer long-term savings through reduced cooling costs, the higher upfront investment can deter consumers from making the switch. Furthermore, the perception of high costs may be exacerbated by a lack of immediate financial incentives or subsidies to encourage adoption.
In addition to the financial factor, some consumers may be reluctant to adopt heat-reflecting paints due to a lack of awareness or understanding of their long-term benefits. While the benefits of energy efficiency are becoming increasingly evident, convincing consumers to invest in these paints can be challenging if they are not well informed about their advantages.
3. Regulatory and Standardization Challenges
As the market for heat-reflecting paints grows, there is a need for standardized regulations and certifications to ensure product quality and performance. However, the lack of consistent standards for heat-reflecting paints can create uncertainty for manufacturers and consumers alike. Without clear guidelines or testing standards, the market could be flooded with subpar products that fail to deliver the expected performance.
Additionally, regulatory challenges related to environmental impact, safety, and performance testing can pose hurdles for manufacturers seeking to enter or expand in the market. Different regions may have varying regulations regarding the use of certain chemicals or materials in heat-reflecting paints, which could complicate product development and compliance. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory landscapes carefully to ensure that their products meet local standards and gain market acceptance.
4. Durability and Maintenance Issues
Another potential threat to the heat-reflecting paints market is the issue of durability and maintenance. While heat-reflecting paints are designed to last for extended periods, factors such as exposure to extreme weather conditions, UV radiation, and pollution can affect their long-term performance. In particular, the reflective properties of the paint may degrade over time, reducing its effectiveness and necessitating reapplication or maintenance.
This issue is particularly significant for exterior applications, such as roofs and walls, which are exposed to the elements on a continuous basis. The need for regular maintenance could undermine the cost-effectiveness of heat-reflecting paints and dissuade potential customers from adopting them. To address this threat, manufacturers must focus on developing more durable formulations that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and maintain their reflective capabilities for longer periods.
5. Lack of Consumer Awareness and Education
Despite the growing popularity of energy-efficient solutions, there is still a significant gap in consumer awareness regarding the benefits of heat-reflecting paints. Many consumers may not fully understand how these paints work or the potential energy savings they can provide. In some cases, they may be unaware that heat-reflecting paints can help reduce the urban heat island effect, lower cooling costs, and improve overall building performance.
The lack of education and awareness can lead to slower adoption rates and limit the overall growth of the market. Manufacturers and industry stakeholders must invest in consumer education initiatives to raise awareness about the advantages of heat-reflecting paints. By offering clear, concise information about the environmental and economic benefits, companies can encourage more consumers to make the switch to these sustainable paints.
6. Climatic and Geographic Limitations
The effectiveness of heat-reflecting paints is largely dependent on the climate and geographic location where they are applied. In regions with cooler climates, where air conditioning is less of a necessity, the demand for heat-reflecting paints may be limited. Similarly, in areas with frequent rainfall or high humidity, the reflective properties of the paint could degrade more quickly, reducing their overall effectiveness.
As a result, the adoption of heat-reflecting paints may be more prevalent in hot and sunny regions where cooling costs are a significant concern. Companies looking to expand into new markets must carefully assess the local climate and geographic factors to determine whether heat-reflecting paints are a viable solution in those areas.
Conclusion
While the heat-reflecting paints market holds substantial potential, several threats must be addressed to ensure continued growth and success. Competition from alternative cooling technologies, high initial costs, regulatory challenges, durability concerns, lack of consumer awareness, and climatic limitations all pose significant risks to the market. By focusing on product innovation, educating consumers, and addressing regulatory challenges, companies can mitigate these threats and continue to drive the adoption of heat-reflecting paints as a sustainable solution for energy efficiency and environmental conservation.