INTRODUCTION
Transformers are essential to the distribution and transmission of electrical electricity. These devices are used to step up or down voltage levels, ensuring efficient Power Transformers with minimal energy loss. There are several varieties of transformers, each intended for a particular use. This article explores different types of transformers, including power, distribution, three-phase, and furnace transformers.
What is a Transformer?
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits via electromagnetic induction. It consists of primary and secondary windings wound around a magnetic core. Depending on its application, a transformer can either increase (step-up) or decrease (step-down) voltage levels, making it an essential component in power transmission and distribution networks.
Power Transformers
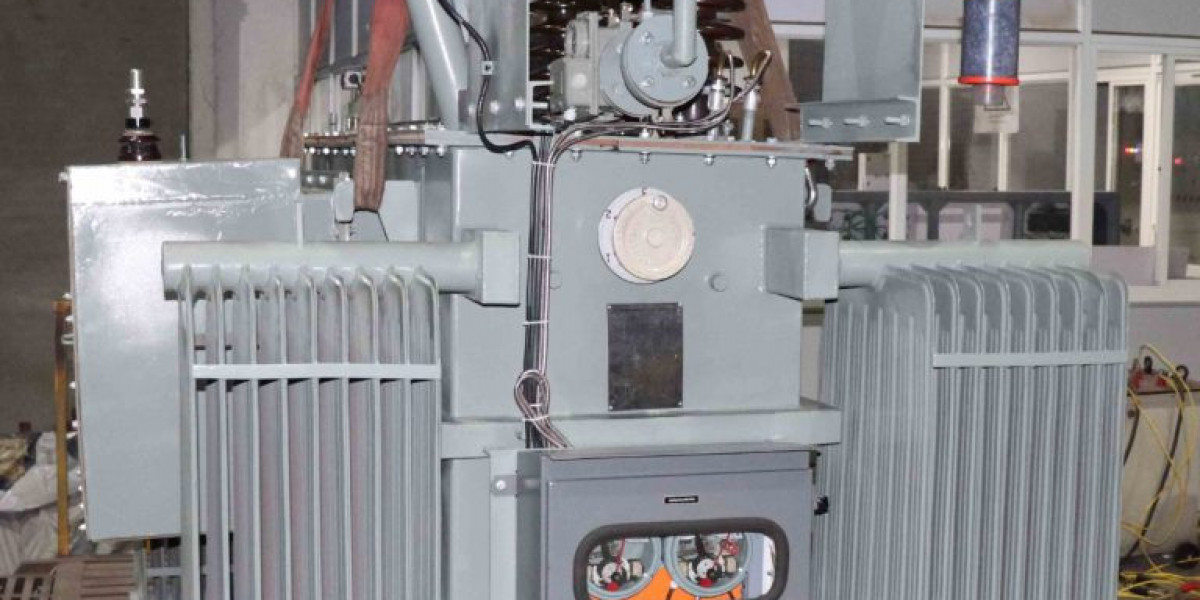
Power transformers are designed for high-voltage transmission networks to step up or step down voltage levels. These transformers operate at maximum efficiency, typically above 95%, and handle large power loads. They are mainly used in substations, power plants, and industrial facilities.
Types of Power Transformers
Step-Up Transformer: Increases voltage from the power generation station before transmitting it over long distances to reduce energy loss.
Step-Down Transformer: Reduces high transmission voltage to lower levels suitable for industrial and domestic use.
Applications of Power Transformers
Power generation stations
High-voltage transmission networks
Industrial applications requiring high power loads
Distribution Transformers
Distribution transformers are used in power distribution networks to step down voltage to levels suitable for end-users. Unlike power transformers, they operate at lower efficiency (typically around 50-70%) as they are used continuously to supply electricity to residential and commercial consumers.
Features of Distribution Transformers
Designed for low-voltage applications (11kV, 6.6kV, or 0.4kV)
Operate continuously at varying load conditions
Have lower efficiency compared to power transformers
Applications of Distribution Transformers
Residential power distribution
Commercial buildings and office spaces
Small industrial setups
Three-Phase Transformers
Three-phase transformers are used in industrial and power transmission applications where three-phase power is required. These transformers consist of three windings connected in star or delta configurations.
Advantages of Three-Phase Transformers
More efficient than using three single-phase transformers
Smaller size and weight, making them cost-effective
Reduced electrical losses in power distribution
Applications of Three-Phase Transformers
Industrial power systems
Large-scale manufacturing plants
Electrical substations
Furnace Transformers
Furnace transformers are specifically designed for electric furnaces that require a high current supply at low voltage. These transformers supply power to arc furnaces used in steel production and other metallurgical processes.
Types of Furnace Transformers
Arc Furnace Transformers: Used in electric arc furnaces for steel melting.
Induction Furnace Transformers: Supply power to induction furnaces for metal heating and melting.
Applications of Furnace Transformers
Steel manufacturing plants
Foundries and metal processing units
High-current applications requiring controlled voltage regulation
Conclusion
Transformers are indispensable components in electrical power systems, ensuring efficient energy transmission and distribution. Power transformers facilitate high-voltage transmission over long distances, while distribution transformers deliver electricity to end-users. Three-phase transformers provide efficient power handling for industrial applications, and furnace transformers supply the high current needed for metal processing. Understanding these transformer types and their applications helps industries and power networks optimize energy efficiency and reliability.