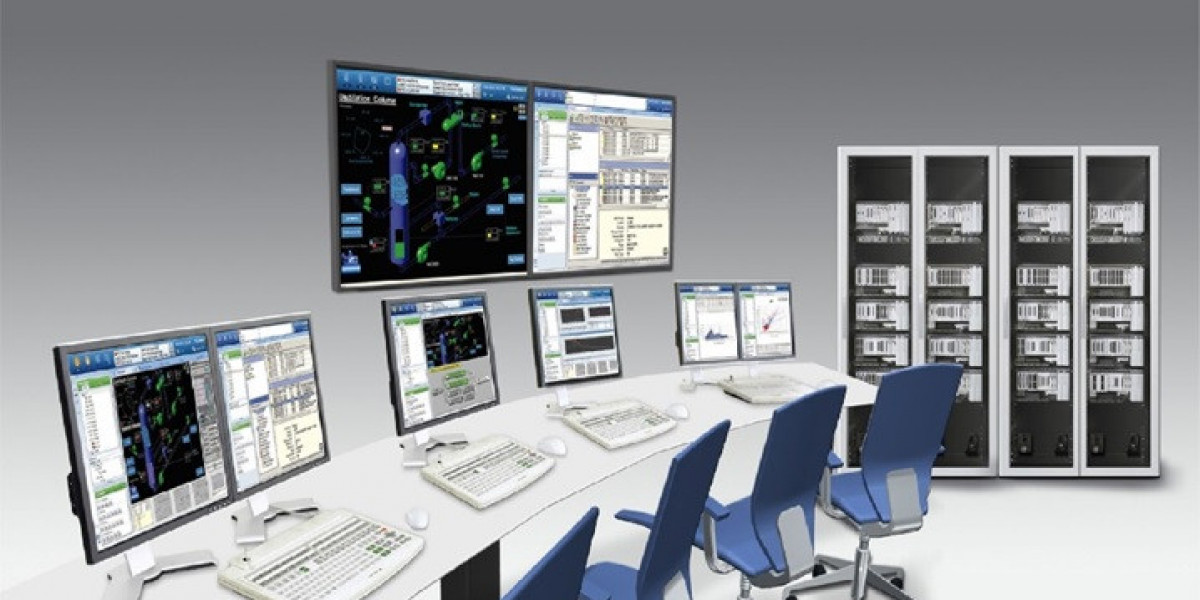
The Distributed Control Systems market plays a pivotal role in modern industrial automation, delivering reliable and scalable control solutions across sectors like oil & gas, power generation, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and more. Despite promising growth driven by Industry 4.0 adoption and expanding automation needs, the market faces several dynamics that restrain its potential and present barriers for new entrants. Understanding these challenges is crucial for stakeholders to navigate the competitive landscape effectively.
This article delves into the key restraints and market entry barriers shaping the Distributed Control Systems market dynamics.
Key Market Restraints
1. High Initial Capital Investment
One of the most significant restraints in the DCS market is the substantial upfront capital expenditure required. Implementing a full-fledged DCS involves costs related to hardware, software, engineering, commissioning, and training. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) or industries in developing regions may find these costs prohibitive, limiting their adoption of advanced control systems.
2. Complexity of Integration with Legacy Systems
Many industrial facilities still operate legacy control systems that are not inherently compatible with modern DCS architectures. Integrating new DCS solutions with outdated infrastructure often requires custom interfaces, additional engineering effort, and can lead to operational disruptions during upgrades. This complexity acts as a deterrent for organizations contemplating system modernization.
3. Cybersecurity Concerns
As DCS platforms increasingly connect to corporate networks and cloud systems, they become vulnerable to cyberattacks. The threat of data breaches, operational sabotage, or ransomware attacks creates hesitancy among end-users to fully embrace connected and cloud-enabled DCS solutions. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures adds to system complexity and costs, restraining market growth.
4. Skilled Workforce Shortage
Operating and maintaining sophisticated DCS solutions requires highly skilled engineers and technicians with expertise in both industrial control and IT domains. A shortage of trained personnel globally restricts effective deployment and ongoing management of DCS platforms, particularly in emerging markets.
5. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Industries governed by strict safety, environmental, and cybersecurity regulations face additional compliance costs and procedural hurdles when adopting or upgrading DCS. Navigating this regulatory landscape requires dedicated resources and expertise, acting as a barrier for some organizations.
Market Entry Barriers
1. High Research and Development (R&D) Costs
Developing competitive DCS solutions demands significant investment in R&D to incorporate advanced features such as AI-driven analytics, IoT integration, cybersecurity protocols, and scalable architectures. New entrants face steep costs and technological challenges to match incumbent players' product quality and reliability.
2. Strong Established Players
The DCS market is dominated by well-established companies like Emerson, Siemens, Honeywell, ABB, Schneider Electric, and Yokogawa. These incumbents benefit from brand reputation, extensive global distribution networks, comprehensive product portfolios, and long-standing customer relationships. New entrants must overcome significant brand loyalty and trust barriers.
3. Certification and Compliance Requirements
Meeting stringent international standards (e.g., IEC 61508 for functional safety, IEC 62443 for cybersecurity) is mandatory for DCS solutions in critical industries. Achieving these certifications requires rigorous testing, documentation, and audits—processes that are time-consuming and expensive for newcomers.
4. Long Sales Cycles and Complex Procurement Processes
Purchasing DCS systems typically involves lengthy evaluation, budgeting, and approval processes due to high costs and critical operational impact. Buyers prefer vendors with proven track records, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction quickly.
5. Customer-Specific Customization Needs
Many industries require DCS solutions tailored to unique operational processes and integration with existing systems. Developing customizable and flexible platforms that cater to diverse client needs demands significant expertise and resources, creating a high barrier for new market players.
Strategies to Overcome Restraints and Entry Barriers
1. Focus on Modular and Scalable Solutions
Offering modular DCS platforms that allow phased investment and gradual expansion helps lower the initial cost barrier for customers, particularly SMEs and emerging markets.
2. Leveraging Cloud and Edge Computing
Incorporating cloud-enabled services and edge computing can reduce infrastructure costs and improve system flexibility, addressing integration challenges and enhancing cybersecurity.
3. Strategic Partnerships and Alliances
Collaborating with established system integrators, technology providers, and local partners can provide new entrants with market access, domain expertise, and credibility.
4. Emphasis on Training and Support Services
Providing comprehensive training programs and robust after-sales support helps bridge the skilled workforce gap, building customer confidence in deploying advanced DCS technologies.
5. Compliance and Certification Investment
Early investment in obtaining relevant safety and cybersecurity certifications builds trust and meets regulatory requirements, easing market entry.
Conclusion
While the Distributed Control Systems market offers vast growth opportunities fueled by industrial automation and digital transformation, it is tempered by significant restraints and market entry barriers. High capital requirements, integration complexities, cybersecurity risks, and regulatory challenges restrict widespread adoption, especially among smaller players and developing economies.